Product Features
-
Exceptional Flexibility: The multi-strand fine-wire structure allows for easy bending, twisting, and routing, making it especially suitable for installations in confined spaces or with complex cable paths.
-
Excellent Conductivity: Manufactured from high-purity electrolytic copper (typically ≥99.9%) and annealed, it ensures low resistance and high-efficiency current transmission, complying with international conductor standards.
-
High Fatigue Resistance & Durability: The stranded design distributes stress, offering a longer service life and higher reliability compared to solid-core wires in applications involving frequent bending, vibration, or movement.
-
Easy & Reliable Installation: The soft nature facilitates manual handling and terminal crimping. Multiple fine strands create a denser connection with a larger contact area under terminals, reducing the risk of hot spots and loosening.
-
Good Heat Dissipation: The small gaps between strands promote air circulation, aiding in heat dissipation during operation.
II. Application FieldsWidely used in critical areas such as complex wiring within distribution cabinets, equipment terminal connections, grounding system jumpers, power supply for mobile equipment, and interconnections in new energy systems. It is particularly suited for demanding installation scenarios with space constraints, presence of vibration, or requiring frequent bending.
III. Structure & Composition
-
Conductor:
-
Material: High-purity electrolytic copper (Cu ≥ 99.9%).
-
Temper: Annealed (softened), transforming it from a hard-drawn to a soft state, which is the key process for achieving flexibility.
-
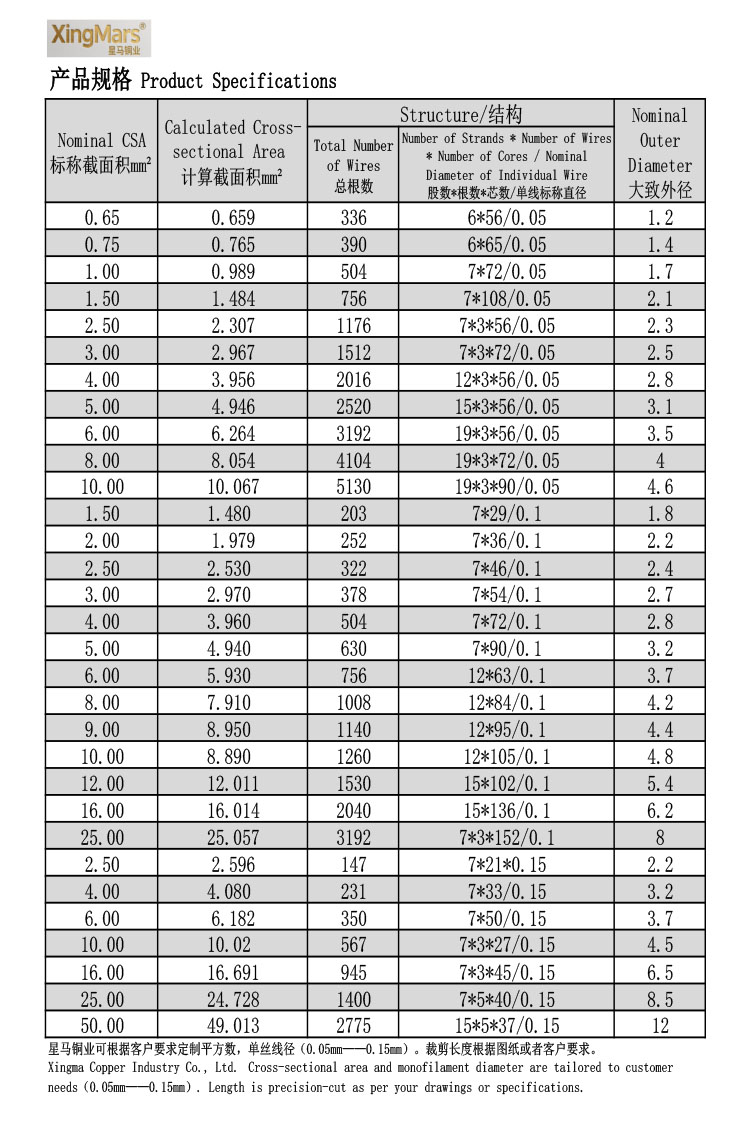
Construction: Composed of numerous (tens to thousands) round copper single wires (strands), with diameters ranging from 0.05mm to 0.2mm. These are helically stranded together, typically in concentric layers. Finer wire diameters and a higher strand count result in greater flexibility.
-
Optional Coatings (Non-mandatory):
-
Bare Copper: Most common, cost-effective.
-
Tinned Copper: A tin layer plated onto the copper wires, primarily providing oxidation/corrosion resistance, improving solderability, and preventing adverse reactions between copper and certain insulation materials.
-
Silver-Plated Copper: Used in specific applications requiring very high-frequency performance or lower contact resistance. Offers optimal performance at the highest cost.
-
Insulation (For insulated wire versions):
-
Materials: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), XLPE (Cross-linked Polyethylene), Rubber (e.g., Silicone, EPR), Fluoropolymers, etc.
-
Function: Provides electrical insulation, basic mechanical protection, and determines the cable's temperature, oil, and weather resistance characteristics.